This H1B visa guide serves as your comprehensive resource for understanding the H-1B visa, a crucial pathway for many international students seeking employment in the United States after graduation. Navigating the complexities of the H1B visa application can be daunting, but this guide aims to simplify the H1B visa process. Whether you are pursuing a bachelor's degree or a master's Degree, understanding the H1B visa requirements is crucial for your success. Everything from eligibility criteria to processing times will be covered, ensuring you have all the information you need to make informed decisions about your future in the U.S.
Understanding the nuances of the H-1B visa, along with some common myths, can significantly enhance your chances of success. By the end of this guide, you will be well-equipped with knowledge and resources to navigate your path toward obtaining an H-1B visa.
What Is the H-1B Visa?
The H-1B visa is a nonimmigrant visa that allows U.S. companies to temporarily employ foreign workers in specialty occupations. These positions typically require a high level of expertise and a relevant degree. For international students, securing an H-1B visa can be a significant step toward building a career in the United States after graduation. These occupations require the theoretical and practical application of a body of specialized fields such as IT, engineering, mathematics, medicine, and more. This visa is particularly popular among international students who wish to remain in the U.S. after completing their studies.
Key Points about the H-1B Visa:
|
Key Point |
Description |
|
Visa Type |
Nonimmigrant work visa. |
|
Validity |
Initially valid for three years; can be extended up to six years. |
|
Sponsorship |
Requires sponsorship from a U.S. employer. |
|
Specialty Occupations |
Positions must require specialized knowledge typically requiring at least a bachelor’s degree. |
|
Numerical Limitations |
Subject to a yearly cap, meaning only a limited number of visas are available each year. This often leads to a lottery system. |
|
Multi-Stage Process |
The application process involves several steps, including filing a Labor Condition Application (LCA) with the Department of Labor (DOL) and a petition with United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS). |
Benefits of the H-1B Visa
The H-1B visa offers several advantages for both employers and employees.
Benefits for Employers:
Employers benefit from hiring foreign workers through the H-1B program by gaining access to a broader talent pool with specialized skills that may not be readily available in the U.S. labor market. This can enhance innovation and productivity within their organizations:
|
Employer Benefits |
Description |
|
Access to Global Talent |
Ability to hire skilled professionals from around the world |
|
Increased Innovation |
Diverse perspectives contribute to creative solutions |
|
Competitive Advantage |
Ability to fill specialized roles that are hard to staff domestically |
|
Fill Skill Gaps |
The visa helps businesses address specific skill shortages within their workforce |
Benefits for Employees:
For employees, obtaining an H-1B visa opens numerous opportunities:
|
Employee Benefits |
Description |
|
Work in the USA |
The opportunity to live and work in the United States in a skilled profession |
|
Pathway to Green Card |
Potential pathways to permanent residency |
|
Career Advancement |
This can lead to career growth and higher earning potential |
|
Professional Development |
Exposure to new environments and opportunities for professional development |
|
Higher Salaries |
Competitive salaries often higher than domestic counterparts |
H1B Visa Cap and the Lottery System
Each fiscal year, USCIS issues a limited number of H-1B visas. The H-1B visa program has an annual cap of 65,000 visas for new applicants, with an additional 20,000 visas available for applicants holding a master’s degree or higher from a U.S. institution. This cap creates a highly competitive process, often involving a lottery system when demand exceeds the cap. This means even if you meet all requirements, there is no guarantee of selection. A separate cap exists for those with a U.S. master's degree or higher, offering a slightly improved chance of selection. The number of available visas is subject to change, so staying updated on USCIS announcements is crucial.
Annual Cap Breakdown:
|
Category |
Cap Limit |
|
Regular Cap |
65,000 |
|
Master’s Degree Exemption |
20,000 |
|
Total Potential Visas |
85,000 |
For further information about the numerical cap, check USCIS H-1B Cap Season page.
The H-1B Lottery Process
Due to high demand exceeding supply, USCIS conducts a lottery system each year during which petitions are randomly selected until reaching cap limits.
Lottery Process Steps:
Steps involved in lottery selection process:
|
Step |
Action Taken |
|
Application Submission |
Petitions accepted during designated period (March-April) |
|
Lottery Selection |
Random selection conducted by USCIS if applications exceed cap |
How Long Does an H-1B Visa Take?
Generally, it takes several months from filing until approval; however, premium processing can shorten this time significantly.
Timeline Summary:
- Application Submission: March
- Lottery Selection: April
- Approval Notification: Varies based on processing method
Overall Timeline Estimate:
- Regular Processing: Up to 6 months
- Premium Processing: Approximately 15 days
Who Files the Petition?
The employer files a petition (Form I-129) with USCIS on behalf of the employee (beneficiary). This is a critical step in the H1B visa application process. The employer is responsible for demonstrating that they meet all requirements, and that the employee is qualified for the position.
Responsibilities of Employers:
|
Responsibility |
Description |
|
Job Offer |
Must provide a valid job offer for a specialty occupation |
|
LCA Filing |
Must file a Labor Condition Application (LCA) with DOL |
|
Petition Submission |
Submit Form I-129 along with required documentation |
New Policies and Considerations for Certain Applicant Groups
Recent policy changes have aimed to streamline the H-1B process for specific applicant groups, including U.S. graduates and DACA recipients. These changes aim to retain talented individuals who have already established their lives in the United States.
Key Changes:
|
Change |
Description |
|
Expanded Eligibility |
More flexible criteria for graduates from U.S. universities |
|
DACA Inclusion |
DACA recipients can now apply under certain conditions |
(Note: It is crucial to check the latest USCIS updates for the most current information on these policies.)
Labor Condition Application (LCA)
Employers must file an LCA with DOL before submitting Form I–129.
LCA Requirements:
Requirements include demonstrating compliance with wage laws:
|
Requirement |
Description |
|
Wage Compliance |
Must pay prevailing wage determined by DOL |
This form is submitted by employers seeking approval from USCIS.
H-1B Visa Requirements: Employer and Employee Responsibilities
The H1B visa requirements are stringent, falling under two main categories: employer and employee.
For the Employer:
Employers must meet specific criteria before filing an H-1B petition:
|
Requirement |
Description |
|
Specialty Occupation Demonstration |
Must demonstrate a need for a worker in a specialty occupation. This requires detailed job descriptions and justification. |
|
Prevailing Wage Determination |
Must pay the prevailing wage for the position, as determined by the Department of Labor. |
|
Labor Law Compliance |
Must comply with all applicable labor laws and regulations. This includes ensuring fair working conditions, avoiding discrimination, and providing appropriate benefits. Failure to comply can lead to petition denial. |
|
Recruitment Evidence |
Must demonstrate recruitment efforts before hiring foreign workers |
For the Employee:
To qualify for an H-1B visa, employees must meet certain educational and professional criteria:
|
Requirement |
Description |
|
Educational Qualification |
Must hold at least a bachelor’s degree or its equivalent. |
|
Specialized Knowledge |
Must have specialized knowledge relevant to the position offered. |
|
Skills and Experience |
Must possess the necessary skills and experience to perform the job duties. This may involve providing evidence of prior employment, projects, or academic achievements. |
|
Intent to Return Home |
Must prove their intent to return to their home country after the visa term concludes. This requires careful documentation and demonstration of ties to their home country. |
Additional Considerations:
Employers must also comply with Labor Condition Applications (LCA), which outline working conditions and wages offered to foreign workers.
How to Apply for an H-1B Visa?
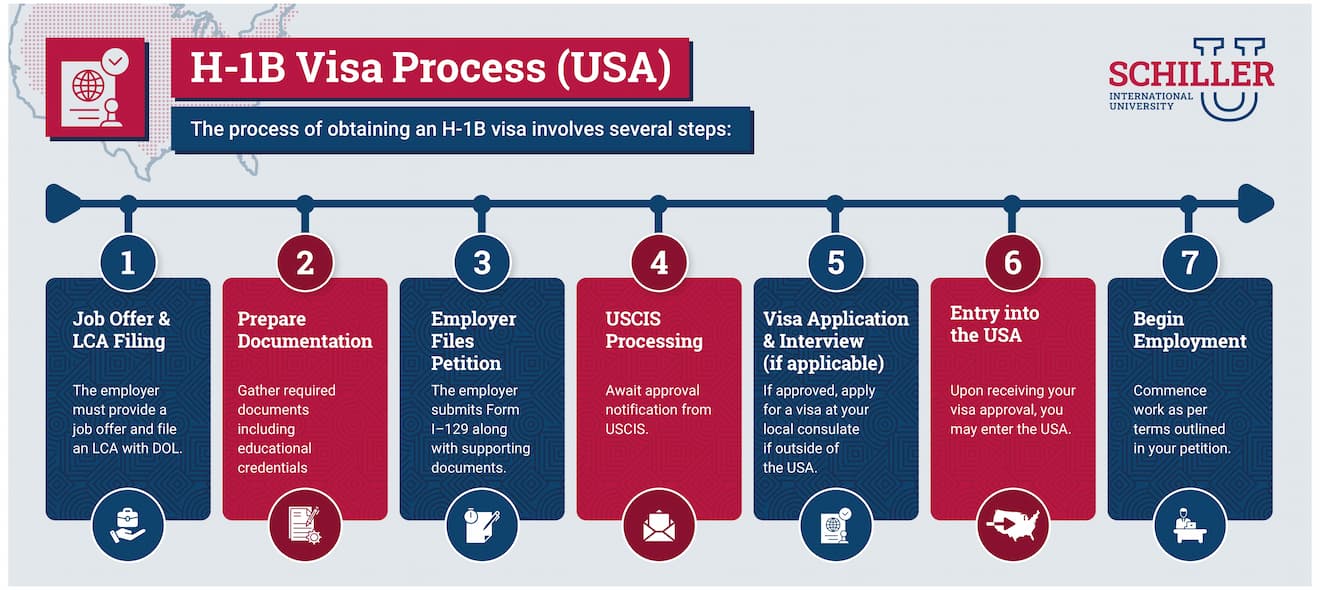
Applying for an H-1B visa is a multi-step process that requires meticulous planning and thorough documentation. Here is a breakdown:
Step 1: Secure a Job Offer:
Find a sponsoring U.S. employer willing to file the H-1B petition on your behalf.
Step 2: Submit your Labor Condition Application (LCA):
The employer files the LCA with the Department of Labor (DOL). This document demonstrates that the employer will not displace any U.S. workers and that they will pay the prevailing wage.
Step 3: Prepare for Form I-129 for H1B Petition:
The employer files Form I-129, Petition for a Nonimmigrant Worker, with USCIS. This petition contains detailed information about the job, the employee, and the employer's commitment to complying with all H-1B regulations. It is crucial to ensure complete and accurate documentation.
Step 4: Employer Files Petition:
The employer will need to submit Form I–129 along with supporting documents such as:
LCA approval notice
Company financial statements
Step 5: USCIS Processing:
USCIS reviews the petition, which can take several months, so, wait for USCIS to process your petition. During this period, USCIS may issue a Request for Evidence (RFE) if additional information is needed.
Step 6: Lottery (if applicable):
If the number of petitions exceeds the annual cap, USCIS conducts a lottery to randomly select petitions.
Step 7: Approval or Denial:
USCIS will issue a notice of approval or denial. An approval notice (Form I-797) allows the employer to proceed with the next steps.
Step 8: Apply for the Visa (If Necessary):
If the employee is outside the U.S., they need to apply for the H-1B visa at a U.S. consulate or embassy in their home country.
Step 9: Visa Interview (If Necessary):
You may have a visa interview, where consular officers assess your eligibility.
Step 10: Entry into the U.S.:
Once the visa is approved, the employee can enter the U.S.
Step 11: Commencement of Employment:
After entry, the employee can begin their employment with the sponsoring employer.
H-1B Specialty Occupations: Defining the Eligible Roles
The H-1B visa applies to "specialty occupations," requiring theoretical and practical application of a body of specialized knowledge and a bachelor's degree or equivalent.
|
Classification |
General Requirements (among others) |
Labor Condition Application Required? |
|
H-1B Specialty Occupations |
To qualify for an H-1B visa for a specialty occupation, the job must require theoretical and practical application of specialized knowledge, normally needing at least a bachelor's degree.
The position itself must also meet one of four criteria:
|
Yes. The prospective petitioner must include a Form ETA-9035/9035E, Labor Condition Application (LCA) certified by the Department of Labor (DOL), with the Form I-129, Petition for a Non-immigrant Worker. For more information see the Information for Employers and Employees page. |
Examples of specialty occupations:
|
Specialty Occupation Category |
Examples |
Required Education/Experience |
|
Engineering |
Software Engineer, Civil Engineer, etc. |
Bachelor’s degree in engineering |
|
Computer Science |
Software Developer, Data Scientist, etc. |
Bachelor’s degree in computer science |
|
Medicine |
Physician, Surgeon, etc. |
Medical Degree, Residency |
|
Accounting |
Certified Public Accountant (CPA), etc. |
Bachelor’s degree in accounting |
|
Architecture |
Architect, Urban Planner, etc. |
Bachelor’s degree in architecture |
|
Science |
Research Scientist, Biologist, etc. |
Bachelor's Degree in Relevant Science |
H1B Visa Documents: A Comprehensive Checklist
The required documents for the H1B visa application are extensive and vary depending on the applicant's situation. Both employers and employees must submit various documents including:
|
Document Type |
Description |
Employer or Employee Responsibility |
|
Form I-129 |
Petition for a Nonimmigrant Worker |
Employer |
|
LCA |
Labor Condition Application |
Employer |
|
Degree Certificates |
Bachelor's degree or higher |
Employee |
|
Transcripts |
Academic transcripts showing course completion |
Employee |
|
Resume/CV |
Detailed resume or curriculum vitae highlighting skills and experience |
Employee |
|
Job Offer Letter |
Formal job offer from the U.S. employer |
Employer |
|
Employer's Business Info |
Documents showing the employer's business structure, financial stability, etc. |
Employer |
|
Passport |
Valid passport with sufficient validity period |
Employee |
|
Passport Photos |
Passport-sized photographs meeting specific requirements |
Employee |
H1B Visa Fees: Understanding the Costs Involved
The fees associated with filing an H-1B petition can vary based on several factors including employer size and whether premium processing is requested.
|
Fee Type |
Amount (USD) |
Responsible |
|
Registration Fee |
$215 |
Employer |
|
Premium Processing (optional) |
$2,805 |
Employer or Employee |
|
Public Law 114-113 Fee |
$4,000 (if 50+ employees) |
Employer |
|
Basic Filing Fee |
$780 $460 for small employers and nonprofits) |
Employer |
|
USCIS Anti-Fraud Fee |
$500 |
Employer |
|
ACWIA Education and Training Fee |
$750 (less than 25 employees) $1,500 (more than 25 employees) |
Employer |
|
Attorney Fee |
Variable |
Employer |
(Note: Fee amounts are subject to change. Always check the official USCIS website for the most up-to-date information.)
Fee breakdown:
- Registration fee: $215 for 2024 season.
- Standard Fee: The standard H-1B filing fee is $780 for the I-129 petition and $460 for small employers and nonprofits.
- American Competitiveness and Workforce Improvement Act (ACWIA) Training Fee: For employers who have 1-25 full-time workers, the fee is $750. For employers with 26 or more full-time employees, the fee is $1,500. Some organizations are exempt including non-profits with affiliations to educational institutions and governmental research organizations.
- Fraud Prevention and Detection Fee: This $500 fee applies to new H-1B petitioners or those changing employers. USCIS requires the sponsoring employer to pay this fee.
- Public Law 114-113 Fee: This H-1B fee applies to companies with upwards of 50 employees with over half on H-1B or L-1 status. The additional fee for these companies is $4,000. However, USCIS may exempt this fee.
- Premium Processing: This service is available to those who want to expedite the H-1B visa process in a 15-day time frame for $2,805. To use this feature, you must complete form I-907. Another optional expense is if family members apply to be H-4 dependents of the applicant by filling out Form DS-160.
- Attorney Fees (vary): H-1B attorney fees differ depending on the firm. Since the stages are now tiered, only certain companies will eventually file the complete petitions.
- Asylum Program Fee: This is a new fee that will be assessed on all Form I-129 and I-140 petitions to help cover the costs of asylum adjudications. This fee should also help free up SCOPS and FOD resources that have been diverted from EB adjudications to asylum adjudications.
- $600 for employers with 26 or more Full-Time Employees (FTEs)
- $300 for small employers (25 FTEs or less)
- $0 for nonprofit organizations
H1B Visa Processing Time: What to Expect
The processing time for an H-1B visa can vary depending on several factors including service center workload and whether premium processing is selected (which expedites processing):
- Time of Year: Processing times tend to be longer during peak application seasons.
- USCIS Workload: High volumes of applications can lead to processing delays.
- Completeness of Application: Incomplete or inaccurate applications may necessitate further review and delay processing.
- Request for Evidence (RFE): If USCIS requires additional evidence, this will extend the processing time.
Typical Processing Times Table:
|
Processing Method |
Estimated Timeframe |
|
Regular Processing |
3 to 6 months |
|
Premium Processing |
15 calendar days |
H-1B Visa to Green Card Pathway
The H-1B visa often serves as a stepping stone toward obtaining a Green Card (permanent residency). This process typically involves additional steps and considerable time. Consult with an immigration lawyer to understand the specifics of your situation.
Green Card Pathways:
Common pathways include employer sponsorship through employment-based categories:
|
Pathway Type |
Description |
|
EB–2 |
For professionals holding advanced degrees |
|
EB–3 |
For skilled workers with at least two years’ experience |
H1B Visa Exceptions and Special Considerations
Certain exceptions and special considerations may apply to the H-1B visa process, depending on your specific circumstances. Always consult the most up-to-date USCIS guidelines.
Amending an H-1B Visa
If there are changes in employment status or job description, employers may need to file an amendment to maintain compliance with USCIS regulations.
Amendment Process Steps:
Steps involved in amending an existing petition:
|
Step |
Action Required |
|
Notify USCIS |
File amended Form I–129 |
|
Provide Updated Documentation |
Include new job description if applicable |
Recapturing Time
H-1B holders may recapture time spent outside of the U.S., potentially extending their stay beyond six years if they have not exhausted their maximum duration.
Recapture Guidelines:
Conditions under which time may be recaptured:
|
Condition |
Description |
|
Time Outside US |
Days spent outside do not count towards maximum stay |
Tips for H-1B Visa Applicants
Actionable tips for prospective applicants:
|
Tip |
Description |
|
Start Early |
Begin preparing your application well before deadlines. |
|
Thorough Preparation |
Meticulous planning and preparation are crucial for a smooth H-1B visa application process. |
|
Accurate Documentation |
Ensure all documents are accurate, complete, and submitted correctly. |
|
Professional Legal Advice |
Consider consulting with an experienced immigration attorney for assistance. |
Common H-1B Myths Debunked
Addressing common misconceptions can alleviate anxiety and help you navigate the process effectively. Seek out reliable sources of information and avoid misinformation. There are many misconceptions surrounding the H-1B visa process. One of the most common myths:
|
Myth |
Fact |
|
Only tech companies hire through H–1Bs |
Many industries utilize this program including healthcare and education |
Summary
The H-1B visa offers a significant opportunity for international students seeking careers in the United States. However, the application process is complex, requiring meticulous preparation and adherence to specific requirements. By understanding the process, preparing thoroughly, and seeking professional advice, when necessary, you can significantly improve your chances of success.
This comprehensive guide serves as your roadmap toward understanding every aspect related specifically towards applying for a H-1B visa successfully under current regulations governing entry into US labor markets!
Glossary of H-1B Visa Terms
Understanding terminology associated with immigration processes facilitate smoother navigation through applications:
Glossary Table:
|
Term |
Definition |
|
Form I–797 |
Notice Action issued by USCIS confirming receipt/approval |
|
Labor Condition Application |
Document filed employers demonstrating compliance wage standards |
|
Prevailing Wage |
Average wage paid employers within specific geographic areas |
|
Adjustment Status |
Process allowing individuals currently residing within US borders change their immigration status |
Frequently Asked Questions:
Question: What is an H-1B visa?
Answer: An H-1B visa allows U.S employers temporarily employ foreign workers specialty occupations requiring specialized knowledge at least bachelor's degree.
Question: How long does it take to get an H-1B?
Answer: Processing times vary but generally take several months unless premium processing selected expedites decisions within 15 calendar days.
Question: Can I apply permanent residency while on an H-1B?
Answer: Yes! Many individuals transition from H-1B status into permanent residency adjustment processes facilitated by their employers.
Question: Is there any cap on how many H-1B visas can be issued?
Answer: Yes! There is an annual cap limiting new applications; currently set at 65k plus additional exemptions available under certain conditions, such as advanced degrees US institutions.
Question: What happens if my H-1B petition gets denied?
Answer: If denied applicants may have options such as appealing decisions depending upon circumstances surrounding denials; consult legal help immediately upon receiving denial notices!

 Apply Now
Apply Now









